Post by : Anees Nasser
The journey of drug discovery stands as one of the most intricate and costly paths in modern healthcare. Crafting a new medicine can span over ten years and demand billions in funding, yet the rates of failure remain alarmingly high during human trials. For a long time, pharmaceutical firms have depended on animal testing to forecast how potential drugs might perform in humans. Unfortunately, the physiological differences between animals and humans often lead to unsafe outcomes and resource misallocation.
This is where Human Organs-on-Chips—small, bio-engineered models that replicate human organ function—step in to revolutionize the landscape. These devices are designed to mimic the structure and physiological characteristics of human tissues, providing a safe, efficient, and ethical alternative for drug testing. Over the past few years, they have progressed from being experimental concepts to essential tools utilized by researchers, biotech firms, and regulatory agencies alike.
Organs-on-chips are heralding a new era in drug testing—a future where scientists can accurately forecast human responses, decrease reliance on animal models, and expedite the transformation from laboratory discoveries into therapeutic solutions.
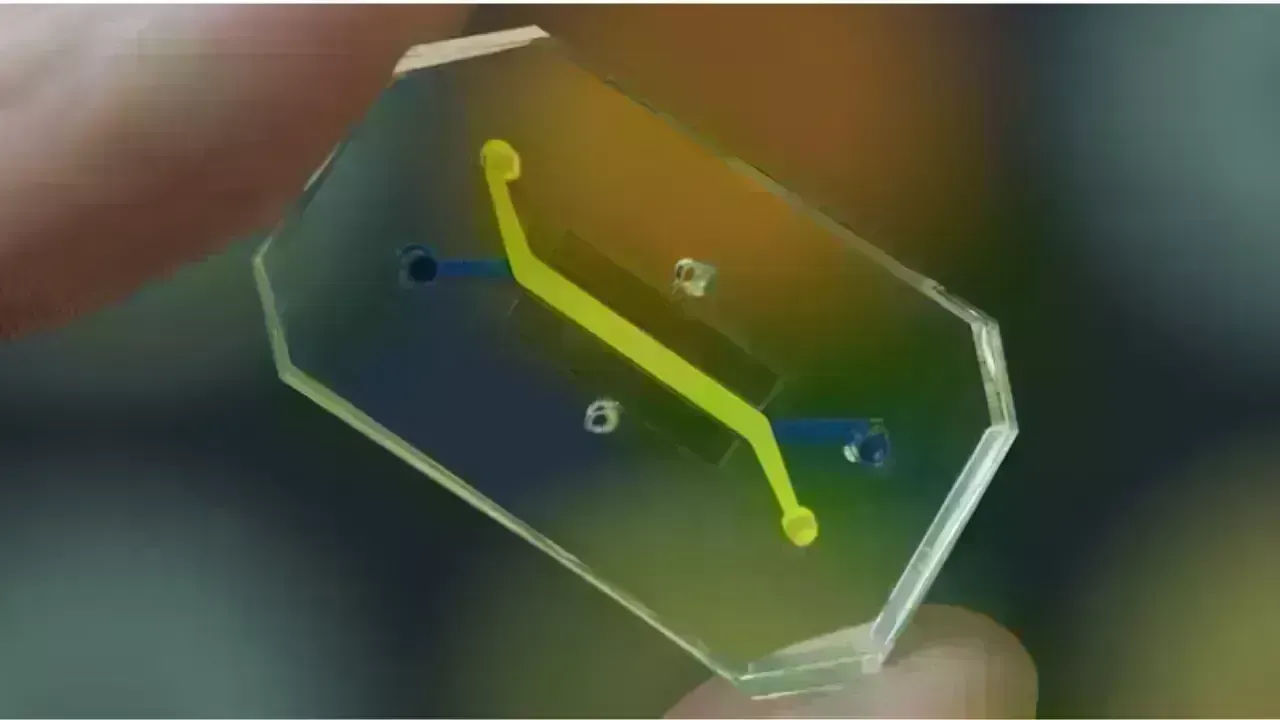
An organ-on-chip is a compact, transparent device—often comparable in size to a USB stick—featuring minuscule channels lined with living human cells. These cells are arranged to echo human tissue patterns, enabling the device to perform organ-like functionalities.
Essentially, these chips integrate:
cell biology
tissue engineering
microfluidics (the precise management of minuscule fluid quantities)
biomechanics
These interconnected elements recreate the native environment of human organs, showcasing blood circulation, mechanical forces, and chemical interactions.
Organs-on-chips can replicate functions like:
the rhythmic expansion and contraction of lungs
the beating of heart tissues
the absorption of nutrients by intestinal tissues
the metabolism of drugs by liver cells
the filtration of toxins by kidney cells
The moving nature of these models distinguishes them from traditional flat laboratory cultures, making them significantly more predictive.
Controversies have long surrounded animal testing, as many drugs deemed safe for animals fall short during human trials due to physiological discrepancies. However, organs-on-chips utilize actual human cells and replicate human physiology, offering markedly more reliable predictions regarding:
toxicity
drug absorption
metabolism
adverse side effects
responses specific to each organ
This could potentially decrease the failure rates during clinical trials while addressing ethical concerns.
Pharmaceutical development is notoriously expensive, often exceeding two billion dollars per drug. A significant portion of this expense arises from failures during earlier or mid-stage testing. The use of organs-on-chips to uncover issues sooner can save:
time
money
human subjects
resources
The ability to simulate human reactions without entering clinical trials at an early stage is a powerful advantage.
Traditional models often struggle to mimic:
rare diseases
genetic issues
individualized health conditions
Organs-on-chips can be tailored using cells derived from patients. This enables:
personalized treatment plans
tailored drug evaluations based on genetic specifics
modeling rare diseases previously impossible to assess in animals
This innovative approach unlocks potential treatments that were once deemed overly complex or prohibitively expensive to explore.
The internal channels of the chip mimic the blood flow in the human body, exposing tissues to nutrients, drugs, and mechanical forces in a realistic manner.
Organs like lungs and intestines continuously undergo motion. Organs-on-chips replicate these forces by stretching and compressing tissues, which enhances precision in drug response forecasts.
Being transparent allows scientists to monitor biological reactions instantly. This encompasses:
cellular responses
tissue damages
inflammatory reactions
patterns of drug absorption
Such real-time insights were never attainable through animal models or traditional laboratory cultures.
One of the inaugural breakthroughs, the lung-on-chip, mimics the rhythmic movements of human lungs. It has been employed to investigate:
respiratory conditions
pollutants in the environment
asthmatic reactions
toxicity effects on lung tissues by drugs
Its precision has fostered partnerships among academic institutions, biotech companies, and regulatory agencies.
Cardiac chips simulate the contractions of heart tissues, enabling examination of:
toxicity of heart drugs
risks of arrhythmia
metabolic processes
the impact of cancer therapies on cardiac cells
These chips are invaluable since cardiac toxicity is a leading reason for drug failures in later stages.
The liver plays an essential role in drug metabolism. Liver chips assist in identifying:
injury caused by drugs to the liver
metabolic pathways
toxicity limits
interactions of enzymes
This chip is critical for screening drugs with potential liver failure risks.
The gut is central to digestion, immunity, and microbiome interactions. These chips allow researchers to explore:
absorptive processes for nutrients
digestive tract diseases
inflammatory bowel illnesses
microbiome reactions to medication
Such information is notably hard to extract via conventional lab models.
The kidney is tasked with waste filtration and fluid regulation. A kidney chip aids researchers in anticipating:
nephrotoxicity (kidney injury)
filtering efficiencies
metabolic responses
Given that kidney toxicity frequently results in drug failures, this model carries significant importance.
Organs-on-chips enable researchers to replicate ailments such as:
metastasis in cancer
viral pathogen interactions
chronic inflammatory conditions
genetic anomalies
This accelerates the discovery of new therapeutics and diagnostic measures.
With tightening global regulations on animal testing, cosmetic corporations and chemical suppliers are shifting toward human model-based assessments. These chips enable the safe testing of:
dermal irritability
chemical effects
allergic responses
without infringing upon ethical standards.
Regulatory bodies are starting to acknowledge the potential benefits of organs-on-chips. They may soon integrate these models into formal drug approval processes, decreasing the reliance on animal test results.
Substantially minimizes or eliminates the requirements for animal experimentation, aligning with global movements toward humane and ethical scientific practices.
Human-centric data yields superior predictions, lowering clinical trial failure rates.
Testing durations are drastically reduced as scientists can execute multiple experiments concurrently.
Chips are customizable with specific:
genetic markers
disease conditions
environmental variables
Such a degree of customization was difficult to achieve before.
Despite their promise, organs-on-chips encounter multiple difficulties:
Creating these chips on a large scale can be costly and technically challenging.
While sophisticated, chips are not yet capable of replicating the entire complexity present within a human organ.
Researchers are refining multi-organ chip designs to simulate the interactions of an entire human body in real-time.
Even with great potential, most drug approval frameworks still heavily depend on animal testing data. Transitioning to chip-based systems necessitates substantial regulatory modifications.
Scientists are now creating connected organ systems-on-chips, where numerous chips work together to mimic the complexity of the entire human organism. This paves the way for:
comprehensive drug simulations
understanding how multiple organ systems respond concurrently
earlier identification of complications
Eventually, integrated systems might replicate:
the immune response
metabolic processes
neurological reactions
This advanced approach brings us closer to a future where drug testing can largely occur virtually before clinical applications.
Human organs-on-chips represent a monumental evolution in biomedical research within the last few decades. Offering ethical, human-relevant, and precise models, this technology has the potential to redefine drug testing in the years ahead.
As the focus shifts towards personalized medicine, reduced animal testing, and expedited therapeutic development, organs-on-chips will become a cornerstone technology shaping the future of groundbreaking medical advancements, whether it’s designing safer medications or predicting patient-specific outcomes.
Disclaimer:
This article is intended for informational and educational purposes and should not be construed as medical or scientific advice.










Dhurandhar Surpasses ₹1000 Cr Globally, Faces Gulf Ban Challenges
Dhurandhar's global earnings exceed ₹1000 crore despite a $10M setback from Gulf bans. Overseas audi

China Asserts Peace Mediation in India-Pakistan Dispute; India Responds Firmly
Amid India's denial of third-party mediation, China claims it helped defuse tensions between India a

Mel Gibson and Rosalind Ross Announce Their Separation After Nearly Ten Years
Mel Gibson and Rosalind Ross reveal their split after nearly a year, emphasizing their commitment to

Rashmika Mandanna and Vijay Deverakonda to Tie the Knot on February 26
Rashmika Mandanna and Vijay Deverakonda are set to marry in an intimate Udaipur ceremony on February

FIFA Upholds 2026 World Cup Ticket Pricing Despite Fan Dissatisfaction
FIFA defends its ticket pricing for the 2026 World Cup, introducing a $60 tier to enhance affordabil

Trump Asserts Role in India-Pakistan Conflict Resolution, India Refutes Claims
Trump asserts he facilitated peace between India and Pakistan, but India firmly denies any US involv