
Post by : Anees Nasser
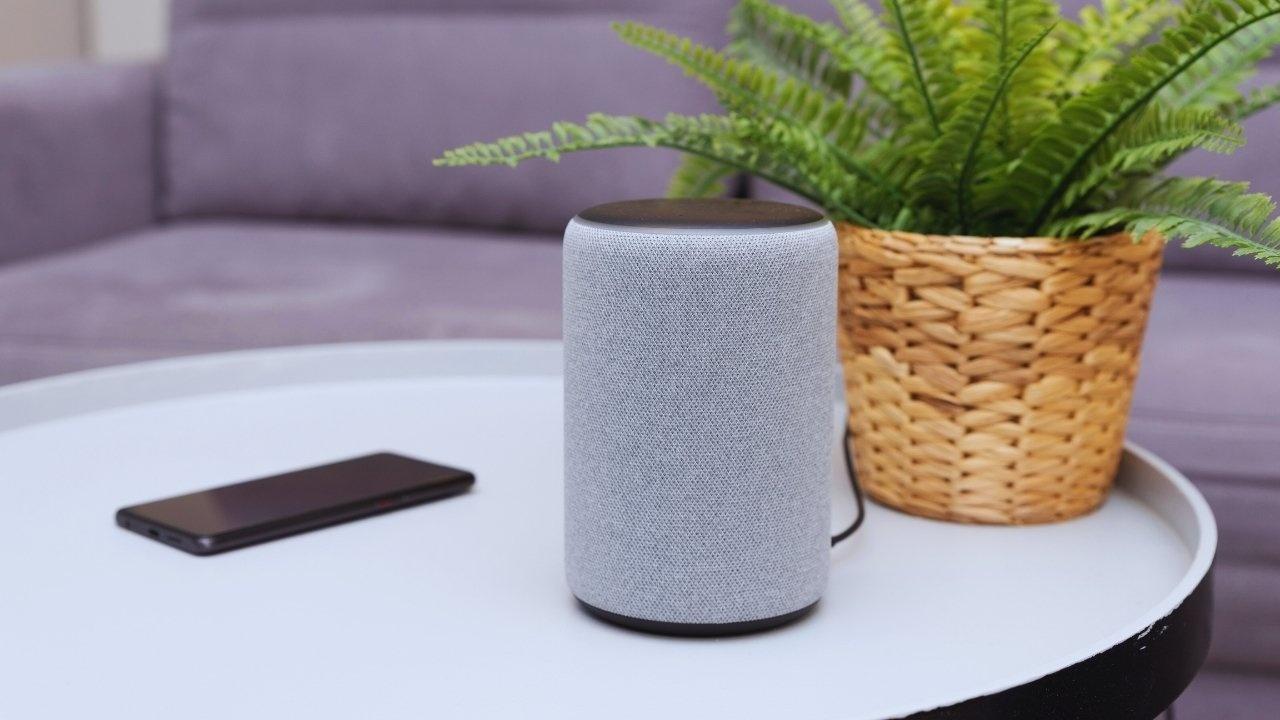
Typically, when one envisions voice assistants, smart speakers in home settings come to mind, serving needs like playing music or managing alarms. However, the landscape for voice technology is experiencing rapid evolution. With advancements in natural language processing, edge computing, improved connectivity, and integrated device ecosystems, voice technology is transitioning from a simple tool to a significant interface in various contexts.
No longer passive, voice technology is becoming proactive and integrated into daily life. It's now included in wearables, vehicles, enterprise applications, retail settings, and industrial IoT. This shift offers tech writers—especially those focusing on Asia and emerging markets—fresh perspectives on device interactions, business adoptions of voice tech, and how certain regions innovate beyond traditional interfaces.
Voice assistants are improving not just in hearing but also in interpreting user commands. Enhanced language models, context recognition, and dialect understanding allow these interfaces to function more effectively in diverse environments.
Rather than depending solely on cloud technology, many voice systems now process data locally or partially locally. This reduces latency, increases reliability without constant internet access, and offers better privacy protections, making it more suitable for regions with limited infrastructure.
From cars and headphones to factory machines and healthcare systems, the range of devices equipped with voice capabilities has expanded significantly. Voice technology is being incorporated into various types of devices, including those typically not considered smart.
Areas where traditional interfaces pose challenges, such as low literacy rates or keypad difficulty, are well-suited for voice technology adoption. In multilingual, mobile-centric societies, voice provides an intuitive system for apps, commerce, and services.
Organizations are discovering that voice interfaces can streamline operations, enhance safety, and facilitate hands-free functioning in fields like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and service industries.
Voice technology is finding its way into devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. These wearables increasingly feature voice commands, situational awareness (considering location and user activity), and proactive features, allowing for context-aware suggestions.
Automobiles serve as a pivotal platform for voice technology. Beyond navigation, voice assistants in vehicles can manage systems, provide contextual advice based on travel patterns, connect with external services (like parking and charging), and integrate with smart city networks, transforming cars into intelligent mobile living spaces.
While smart speakers still hold value, voice interfaces are now penetrating numerous connected devices within homes, encompassing air conditioning, appliances, security systems, and lighting. The smart home hub is evolving into a comprehensive voice-enabled ecosystem.
Voice technology is making significant strides in shopping and customer service. In retail environments, voice-enabled devices assist customers in obtaining information, checking stock, and conducting transactions seamlessly. E-commerce is experiencing rapid growth in voice search and purchasing, particularly in multilingual markets.
Inside warehouses and manufacturing setups, voice interfaces enable workers to remain hands-free, collect data vocally, receive instructions, and interact with systems while physically engaged. This transition moves voice from merely an optional feature to a core interface necessity.
In areas with significant mobile usage and linguistic diversity, voice technologies are evolving into forms like voice search and vernacular-based services, minimizing the need for typing and focusing on natural speech interactions.
Effective voice integrations must deliver immediate and accurate feedback. Any delays or errors can negatively affect user experiences. Intelligent integrations will utilize local processing or hybrid systems to ensure efficiency.
Especially concerning wearables or home devices, systems that prioritize local processing or limit data uploads to the cloud can foster user trust. Users prefer assurances that their verbal interactions are secure and not misused.
The leading voice systems will remember context such as user location, past interactions, and preferences. They will not merely respond but will proactively anticipate user needs.
Voice functionalities will frequently integrate with visual cues, gestures, and other inputs. Potent integrations will link voice technology with broader device networks, enhancing interactions beyond simple commands.
In markets like India and Southeast Asia, voice technology must accommodate numerous languages and dialects. The progression of voice systems in these regions will rely heavily on localization.
For companies adopting voice interfaces, the pivotal question shifts from “Can we use voice?” to “How does it fit into our workflow, enhance customer journeys, and improve overall outcomes?” Voice is increasingly pivotal as a strategic tool.
A leading smart speaker brand is integrating its assistant with major home automation and lighting systems for broader control beyond mere music playback.
Innovative wearable tech that listens to surroundings and offers prompts based on observed context, such as movement or engagement.
Automotive brands embedding voice systems capable of suggesting driving routes, parking spots, and collaborating with smart city services.
Retail kiosks that allow customers to interact using their native languages for transactions or service assistance.
Industrial maintenance setups where technicians can verbally check machinery status, log work, or receive guidance without interrupting hands-on tasks.
The expansion of voice technology holds particular importance in this area due to:
Large mobile-first demographics where conventional typing and interfaces can be challenging.
A multitude of languages and dialects that allow voice to offer better accessibility compared to text.
Increasing smart home and IoT markets leading to more interconnected devices.
Business sectors emphasizing vernacular user interfaces in retail and services.
Voice technology adoption in these markets is likely to supersede traditional UI frameworks, presenting fresh services methodologies.
Challenges persist, such as noisy settings, multiple speakers, regional accents, and linguistic blends that complicate voice recognition.
Wearable devices and IoT networks necessitate greater power, improved connectivity, and the potential need for new hardware. In areas with emerging markets, decisions around retrofitting versus purchasing new devices can be crucial.
Always-on devices raise critical questions about data management: How is data stored, used, and can users disable them?
Voice systems must operate in conjunction with apps, APIs, firmware, and enterprise systems, presenting complex integration and cost challenges.
For voice to become a primary interface, users must their trust in the technology and be willing to alter their usage behavior. Devices must consistently provide value to encourage this transition.
Firms need to determine authentic benefits from voice advances: savings, enhanced customer experiences, or new services, rather than simply adding voice functionality for novelty.
Feature stories examining specific voice tech integrations (in wearables, automotive, or enterprise sectors).
Regional case studies focusing on voice tech adoption across India, Southeast Asia, or Africa.
Explore how businesses are increasingly viewing voice technology as a strategic asset rather than a simple gadget.
Delve into technical nuances: edge voice processing, local language frameworks, and interconnected voice ecosystems.
Reflect on social implications including accessibility, privacy, and new user demographics.
Future perspectives concerning voice technologies: potential developments like silent speech or gesture and voice integration.
Voice technology is no longer confined to smart speakers in living rooms; it is now integrated into wearables, vehicles, work environments, retail spaces, and the broader regional landscape that seeks intuitive interfaces.
This evolution presents consumers with richer, more intuitive functionalities and provides businesses with a new interface layer that enhances efficiency and differentiation. For content creators, the narrative shifts from merely discussing “which speaker” to exploring “which environment” and the “value created.”










Kazakhstan Boosts Oil Supply as US Winter Storm Disrupts Production
Oil prices inch down as Kazakhstan's oilfield ramps up production, countered by severe disruptions f

Return of Officer's Remains in Gaza May Open Rafah Crossing
Israel confirms Ran Gvili's remains identification, paving the way for the Rafah border crossing's p

Border 2 Achieves ₹250 Crore Globally in Just 4 Days: Sunny Deol Shines
Sunny Deol's Border 2 crosses ₹250 crore in 4 days, marking a significant breakthrough in global box
Delay in Jana Nayagan Release as Madras HC Bars Censorship Clearance
The Madras High Court halts the approval of Jana Nayagan's censor certificate, postponing its releas

Tragedy Strikes as MV Trisha Kerstin 3 Accident Leaves 316 Rescued
The MV Trisha Kerstin 3 met an unfortunate fate near Jolo, with 316 passengers rescued. The governme

Aryna Sabalenka Advances to Semi-Finals, Targeting Another Grand Slam Title
Top seed Aryna Sabalenka triumphed over Jovic and now faces Gauff or Svitolina in the semi-finals as