
Post by : Anees Nasser
Agriculture has always been the foundation of human civilization, but today it is also becoming a field where advanced technologies are transforming traditional practices. In Saudi Arabia, where arid lands and extreme temperatures pose challenges for farming, the adoption of smart technologies is no longer a luxury—it is a necessity. One of the most significant innovations shaping agriculture is the Internet of Things (IoT). By connecting sensors, drones, and automated systems to monitor and manage crops, IoT is revolutionizing the way Saudi farms operate. This transformation is not just improving yields but is also setting the stage for sustainable agriculture in a region where water scarcity and climate change remain pressing concerns.
The concept of IoT is relatively simple yet highly impactful. It refers to a network of connected devices that collect and share data in real time. In agriculture, this means deploying soil sensors, climate monitors, and automated irrigation systems that provide farmers with immediate insights into crop health, water usage, and environmental conditions.
For Saudi farmers, these technologies are especially valuable. The country’s agricultural sector faces immense challenges such as limited arable land, reliance on groundwater, and the need to balance food security with sustainable resource use. IoT bridges this gap by providing data-driven solutions, allowing farmers to optimize inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Saudi Arabia’s harsh climate means farming is often an uphill battle. Rainfall is scarce, summers are long and extremely hot, and fertile soil is limited. Traditional farming methods rely heavily on irrigation, consuming vast amounts of water from underground reserves. Over time, this has placed stress on the kingdom’s natural resources.
With a rapidly growing population and the government’s drive to achieve self-sufficiency in food production, modern farming methods have become crucial. IoT helps Saudi farmers overcome these challenges by enabling precise water management, reducing wastage, and improving overall crop resilience. By adopting smart farming, the country is aligning its agricultural practices with its long-term vision for sustainability and food security.
Smart farming in Saudi Arabia takes many practical forms, each designed to tackle specific agricultural challenges. Some of the most common IoT applications include:
Soil Monitoring Sensors: Devices placed in the soil measure moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. Farmers can use this data to decide when and how much to irrigate, ensuring water is not wasted.
Automated Irrigation Systems: These systems, often connected to mobile apps, adjust water supply in real time based on sensor data. This ensures optimal hydration for crops while conserving water resources.
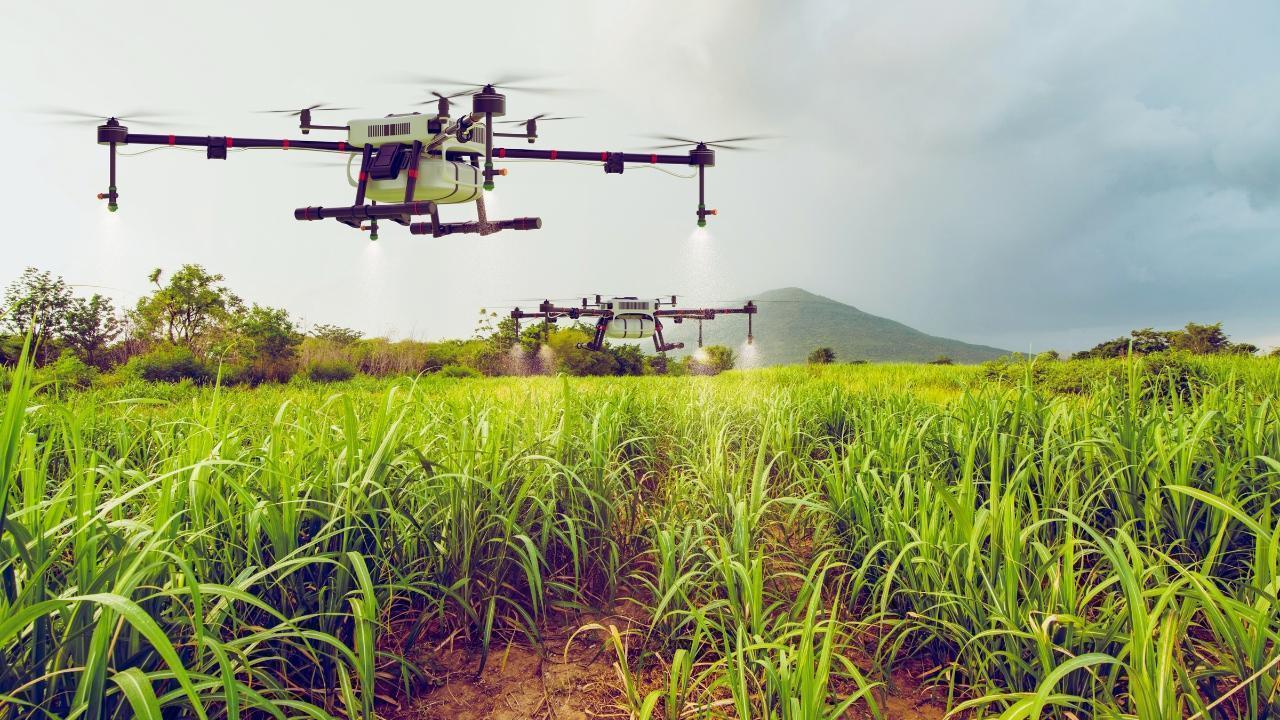
Drones and Aerial Monitoring: Drones capture high-resolution images to detect early signs of disease, pest infestations, or water stress in crops. They provide a bird’s-eye view of farm health that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Livestock Tracking: Beyond crops, IoT also benefits animal farming. Wearable devices track cattle health, feeding habits, and movements, helping farmers monitor productivity and detect illnesses early.
Climate Stations: Weather-monitoring devices predict changing climate conditions, allowing farmers to take preventive measures before a heatwave, sandstorm, or drought affects production.
The shift toward IoT in Saudi farms is not just about technology—it is about tangible economic and environmental benefits.
Water Conservation: IoT enables precision irrigation, cutting down on unnecessary water use. Given the water scarcity in Saudi Arabia, this is one of the most valuable advantages.
Higher Crop Yields: By giving farmers accurate insights into soil and crop health, IoT helps them make better decisions, leading to healthier plants and higher productivity.
Reduced Costs: Automation reduces dependency on labor and minimizes the overuse of expensive resources like fertilizers and pesticides.
Sustainability: By using fewer resources more efficiently, Saudi agriculture becomes more sustainable, aligning with the kingdom’s environmental goals.
Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 emphasizes diversification of the economy, reducing dependency on oil, and promoting sustainable development. Agriculture plays a key role in this strategy, and IoT is central to the modernization of the sector.
Government-backed initiatives and partnerships with global tech companies are making IoT adoption easier for local farmers. Subsidies for modern equipment, training programs, and digital infrastructure investments ensure that even small and medium-scale farmers can integrate these technologies. This support has led to the creation of smart agricultural hubs where innovation thrives.
Despite the progress, implementing IoT in Saudi agriculture is not without hurdles. The main challenges include:
High Initial Costs: IoT devices and systems can be expensive, particularly for smaller farms. Although long-term benefits outweigh the costs, upfront investments remain a concern.
Technical Knowledge: Farmers need training to operate IoT tools effectively. Without proper knowledge, even the most advanced systems may go underutilized.
Connectivity Issues: Some rural areas still lack strong internet connectivity, limiting the effectiveness of IoT solutions.
Data Security: With increased digitalization comes the risk of cyber threats. Protecting farm data from misuse is becoming an emerging challenge.
Several pilot projects in Saudi Arabia demonstrate how IoT is reshaping agriculture:
Greenhouse Farms in Al-Qassim: Farmers in the Al-Qassim region are using smart greenhouses equipped with climate sensors and automated irrigation, significantly improving water efficiency.
Date Palm Cultivation: Since dates are a staple of Saudi agriculture, IoT systems have been introduced to monitor soil and irrigation for date palm trees. This has improved the quality and export value of dates.
Dairy Industry Advances: IoT-powered wearable sensors track the health of dairy cows, resulting in higher milk production and healthier livestock.
These examples highlight how smart farming can be scaled to meet the needs of different types of agriculture.
The future of Saudi agriculture is undoubtedly intertwined with technology. As IoT continues to evolve, integration with artificial intelligence, robotics, and big data will take farming to new levels of precision and efficiency.
In the coming years, Saudi farms could see fully automated greenhouses, AI-driven crop disease detection, and drone fleets managing large-scale farms with minimal human intervention. These developments will help Saudi Arabia not only meet its domestic food requirements but also strengthen its position in the global agricultural trade.
Saudi Arabia’s adoption of IoT also serves as a model for other arid regions across the world. If a country with some of the most challenging agricultural conditions can use IoT to create sustainable farming systems, it sets an inspiring example for others. Countries in Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia facing similar climate challenges can adopt lessons from Saudi Arabia’s smart farming journey.
While the rapid rise of IoT in agriculture is exciting, it is also important to balance modern technology with traditional farming wisdom. Many Saudi farmers come from generations of agricultural knowledge that should not be overlooked. Combining this traditional experience with modern IoT systems creates a holistic approach that is both innovative and rooted in culture.
IoT has become more than just a buzzword in Saudi Arabia—it is a practical solution transforming the agricultural landscape. From conserving water to boosting yields and ensuring sustainable growth, the technology offers immense benefits. Supported by Vision 2030 and driven by necessity, Saudi farmers are proving that innovation and tradition can go hand in hand to create a smarter future for agriculture.
Saudi Arabia’s journey in embracing IoT for agriculture highlights the nation’s resilience and commitment to sustainability. As challenges of climate change and food security intensify worldwide, the lessons from Saudi smart farms are not just relevant locally but globally.
This article is intended for informational purposes only. It highlights general trends and insights into the role of IoT in Saudi Arabian agriculture and should not be considered as specific investment, business, or policy advice. Readers are encouraged to consult industry experts or official sources before making decisions related to agriculture or technology adoption.
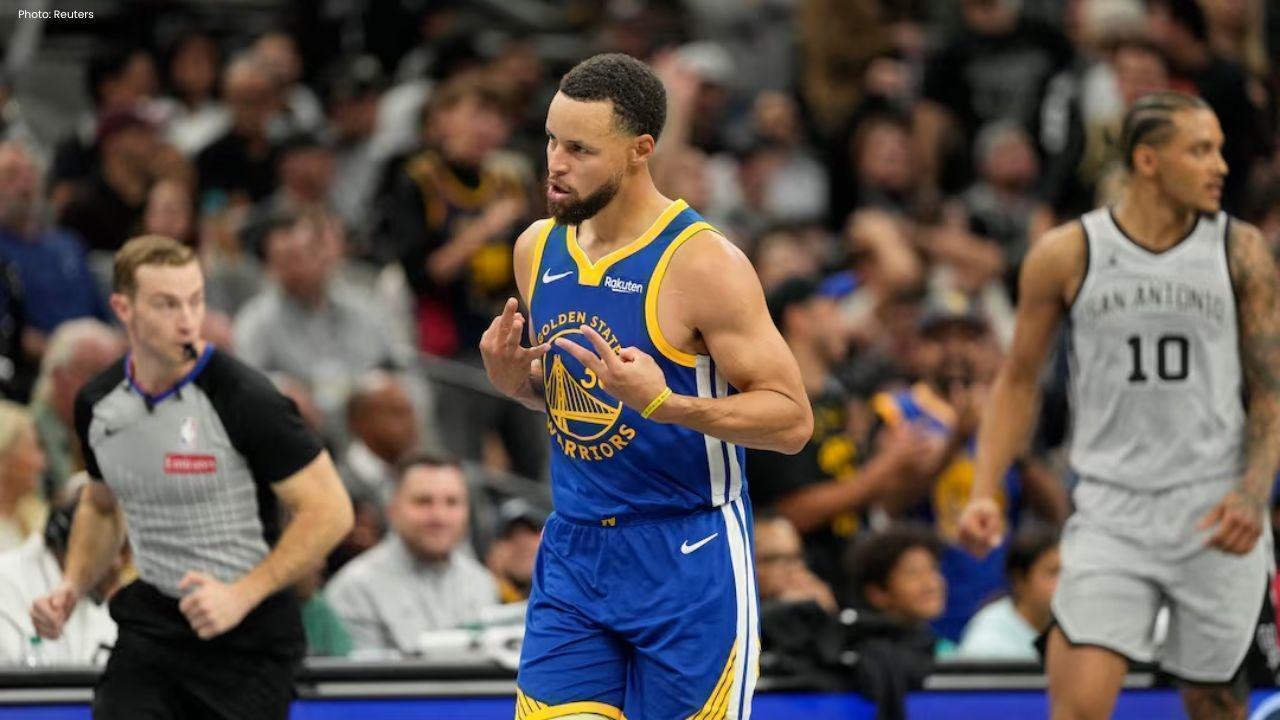









Curry Powers Warriors to Nail-Biting 109-108 Victory Against Spurs
Stephen Curry's 49 points propel the Warriors to a dramatic 109-108 NBA Cup triumph over the Spurs,
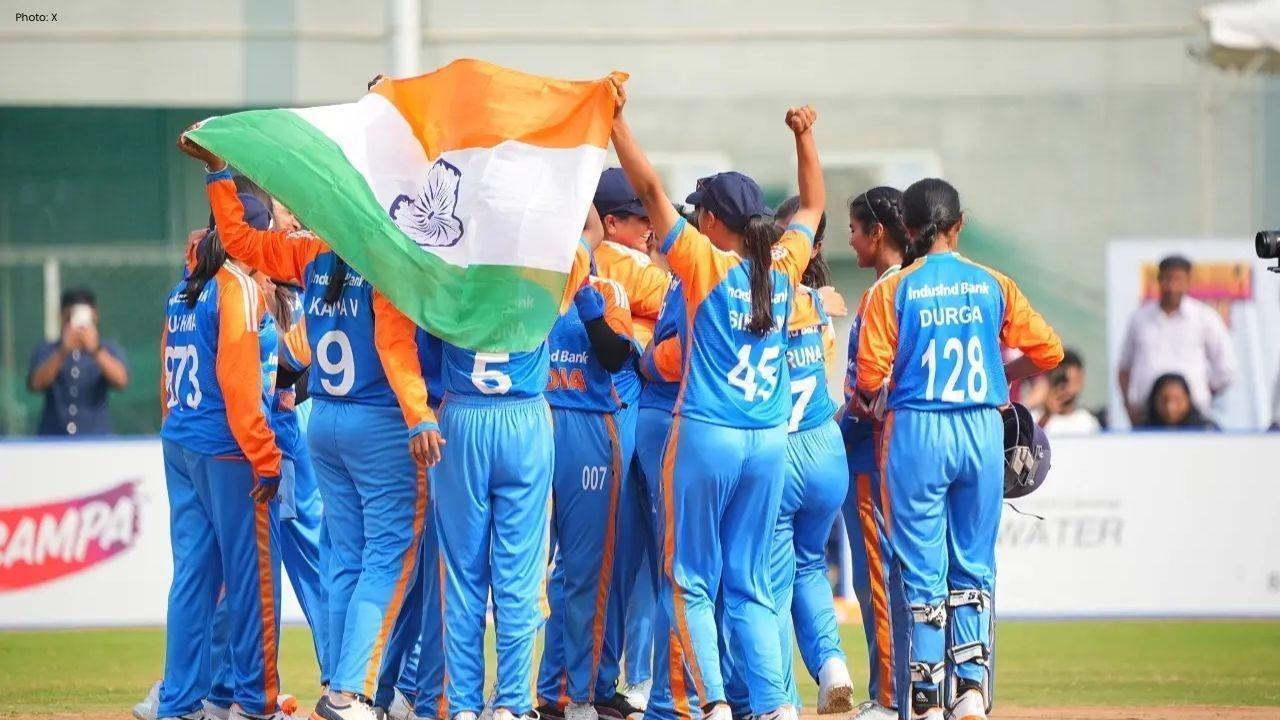

India Advances to Semi-Finals After Thrashing USA in Women’s Blind T20 World Cup
India secured a dominant ten-wicket victory over the USA, advancing to the semi-finals in the Women’

South Africa's Early Advantage as India Struggles on Day Two
On Day Two, India reached 138-4 as South Africa took three early wickets, complicating matters with
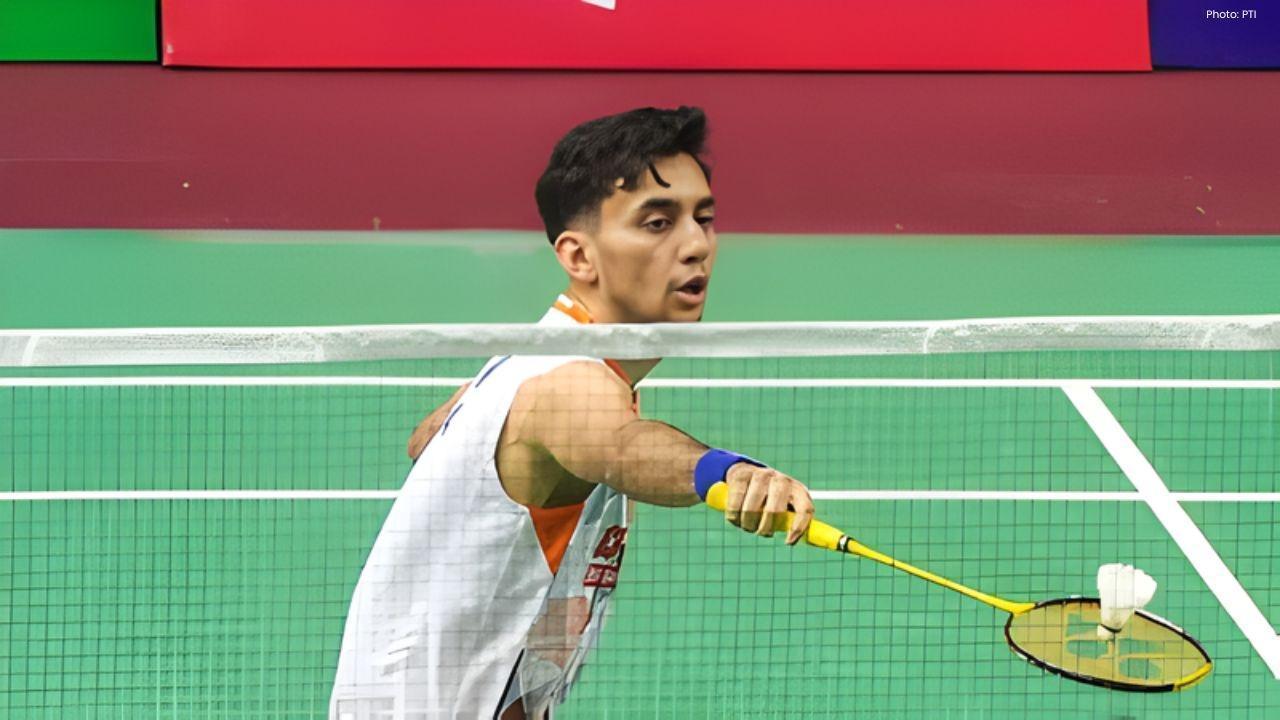

Kenta Nishimoto Defeats Lakshya Sen in Japan Masters Semifinal
Lakshya Sen's journey in the Japan Masters ends after losing to Kenta Nishimoto 19-21, 21-14, 12-21
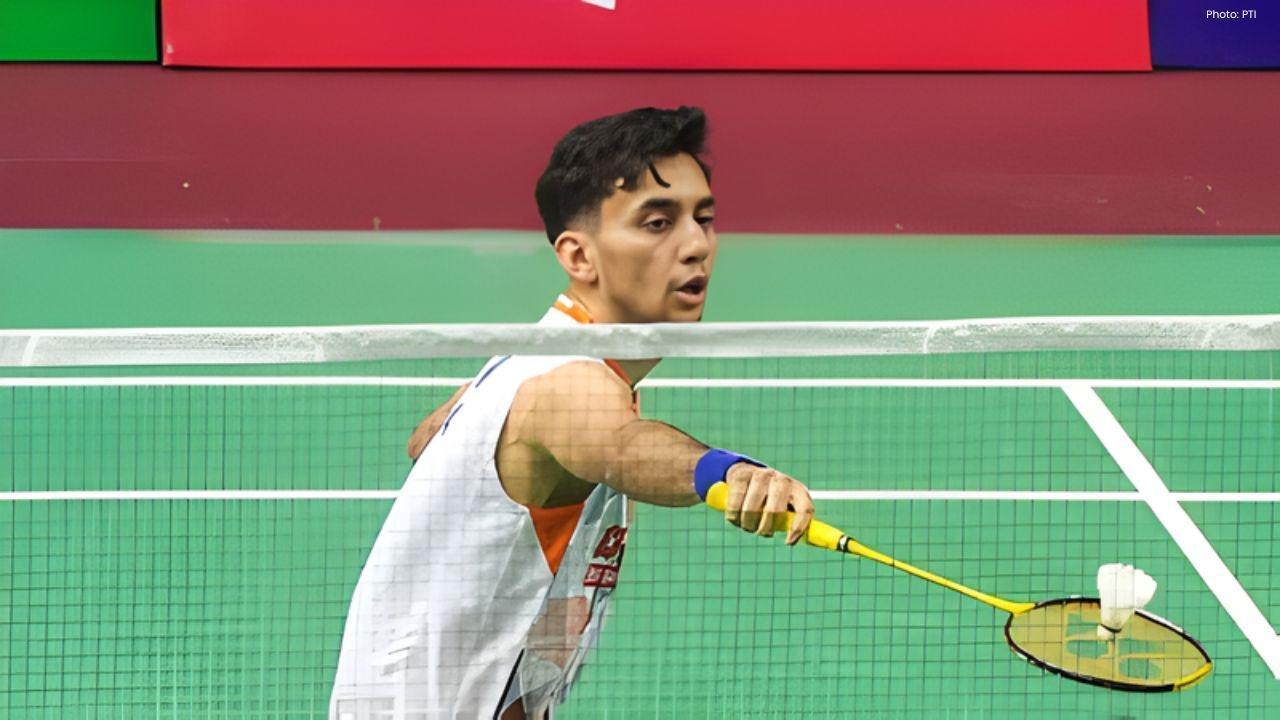

Kenta Nishimoto Defeats Lakshya Sen in Japan Masters Semifinals
Lakshya Sen's run at the Japan Masters concludes with a loss to Kenta Nishimoto in the semifinals, 1
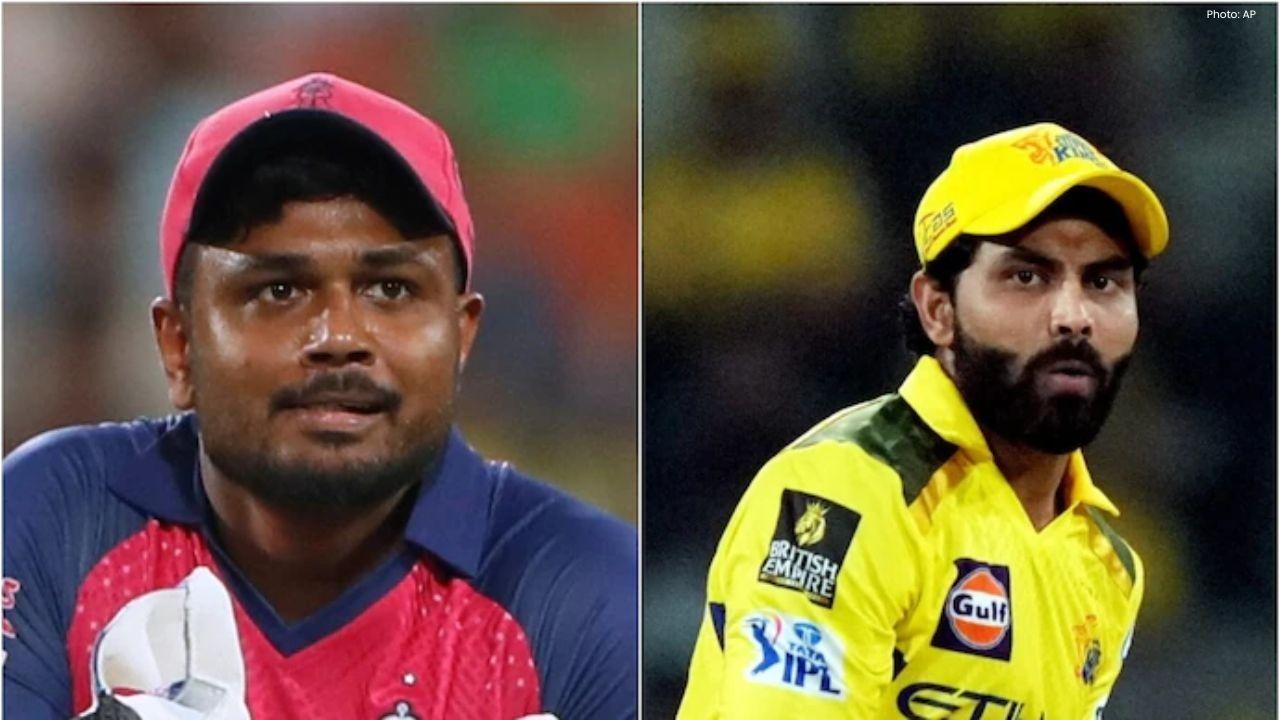

Major IPL Trade: Jadeja Joins Royals as CSK Signs Samson
In a significant IPL trade, CSK has acquired Sanju Samson from Rajasthan Royals in exchange for Ravi