
Post by : Monika
Photo: Reuters
On September 5, 2025, Google was fined €2.95 billion (approximately $3.45 billion) by the European Union for breaking competition rules in its online advertising business. This fine is the fourth major penalty Google has faced in Europe in recent years. The European Commission, which enforces competition law in the EU, said Google used its dominant position in online advertising to unfairly favor its own services.
The EU specifically accused Google of giving an advantage to its ad exchange platform, called AdX. AdX is a platform where advertisers and website owners buy and sell advertising space. The Commission said Google made it harder for other ad platforms to compete fairly. This, in turn, affected publishers, who earn money by displaying ads on their websites.
Background of the Investigation
The investigation began after complaints from the European Publishers Council. This council represents news and media companies across Europe. They claimed Google’s practices hurt both advertisers and consumers. By favoring its own platform, Google reduced competition in the online advertising market, which could lead to higher prices and fewer choices for advertisers.
The EU has been closely monitoring tech companies for years. It wants to ensure that big companies like Google do not use their power to block smaller competitors. Competition law is designed to make sure markets are fair, prices are reasonable, and consumers benefit from choice.
Details of Google’s Practices
According to the EU, Google used its AdX platform in a way that gave it an unfair edge. For example, Google made it more difficult for publishers to use other ad exchanges. This meant that advertisers had fewer options, and publishers had fewer opportunities to sell their ad space at competitive prices.
The Commission said Google’s behavior was deliberate. It wanted to control the advertising market by making its own platform more attractive while making it harder for rivals to succeed. Over time, this could harm competition, which is illegal under EU rules.
Google’s Response
Google immediately responded to the fine, stating it plans to appeal the decision. The company said the European Commission’s ruling is unfair and could harm European businesses, including small and medium-sized companies that rely on Google’s ad services.
Google argued that its advertising tools actually help both advertisers and publishers. Advertisers can reach the right audience more effectively, and publishers can earn money from displaying ads. Google claimed that it did not break any competition laws and that the fine is too large compared to the alleged harm.
Political Reactions
The EU’s decision drew attention in the United States as well. U.S. President Donald Trump criticized the fine, calling it “unfair” and “discriminatory.” He said the penalty could hurt American companies operating in Europe and threatened to respond with trade actions if necessary.
President Trump mentioned Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974. This law allows the U.S. government to take action against foreign countries that engage in unfair trade practices. He warned that the U.S. might consider penalties against the EU if American companies are treated unfairly.
Implications for the Global Tech Industry
The fine against Google is significant for the technology and digital advertising industry worldwide. It shows that regulators are paying closer attention to how big tech companies operate. Online advertising is a fast-growing business, and companies like Google have a large influence over it.
If other countries follow the EU’s example, tech companies could face more fines or stricter rules in multiple regions. This could change how digital advertising works and make companies more careful about how they compete in the market.
Impact on Advertisers and Publishers
The EU’s decision affects not only Google but also advertisers and publishers across Europe. Advertisers might face more competition, which could influence prices for ad space. Publishers could benefit if competitors are allowed a fair chance in the ad market, as it may increase the revenue they earn from ads.
However, if Google appeals the fine successfully, the status quo may continue. Many publishers and advertisers rely on Google’s platform for their day-to-day operations. Any major changes could take time to implement and could affect revenue streams temporarily.
EU’s Commitment to Fair Competition
The European Commission has repeatedly stated that its goal is to protect consumers and businesses. It wants to prevent dominant companies from using their power to unfairly block competition. In Google’s case, the Commission found that the company’s practices limited competition in the online advertising market, which goes against EU competition law.
This approach is part of a broader EU strategy to regulate big tech companies. Over the past decade, the EU has imposed fines on Google, Apple, Amazon, and other major tech companies. Each case focuses on ensuring that large companies do not exploit their dominant positions.
Previous Google Fines in Europe
Google has faced several large fines in the EU before this latest case. These fines include penalties for manipulating search results, favoring its own services, and restricting competitors. In total, the previous fines exceeded €10 billion, showing that European regulators are serious about enforcing competition laws.
The current fine of €2.95 billion focuses specifically on Google’s online advertising practices. It sends a clear signal that the EU intends to maintain a level playing field for all companies, regardless of size.
Potential Outcomes of the Appeal
Google’s appeal could take months or even years to resolve. If the company wins the appeal, the fine could be reduced or canceled. This would allow Google to continue its ad practices as before.
If the EU wins, Google may have to change how it operates its ad exchange platform. This could open opportunities for competitors and change how advertising revenue is distributed among publishers and advertisers. The ruling could also serve as a precedent for other cases involving large tech companies in Europe and beyond.
Global Trade and Diplomatic Implications
The fine has implications beyond the tech industry. It could influence trade and diplomatic relations between the U.S. and the EU. American companies may feel that they are being unfairly targeted by European regulations. This could lead to negotiations or discussions on international trade rules related to digital markets.
The U.S. government has a history of monitoring European actions that affect American businesses. President Trump’s comments reflect concerns that European penalties could be seen as discriminatory. Trade tensions could rise if similar fines are imposed on other U.S. tech companies in Europe.
The €2.95 billion fine against Google marks a major event in the ongoing regulation of big technology companies. It highlights the European Union’s commitment to maintaining fair competition in the digital economy.
For Google, the fine represents both a financial and reputational challenge. How the company responds and whether it successfully appeals will be closely watched by regulators, competitors, advertisers, and publishers worldwide.
The case emphasizes the importance of competition law in the digital era. It also shows that dominant tech companies are under constant scrutiny, and their business practices must meet regulatory standards in multiple regions.
As the digital advertising market continues to grow, this case may influence how companies operate globally, how advertisers and publishers interact with platforms, and how governments enforce competition rules. It is a reminder that even the largest and most influential companies must follow rules designed to protect fair business practices and consumer choice.
The outcome of Google’s appeal will be significant, not only for the company but for the entire technology industry. It could reshape the rules of competition and set a precedent for future regulatory actions against major tech firms in Europe and worldwide.










Alibaba Cloud Leads China’s AI Market with 36% Share
Alibaba Cloud captured over one-third of China’s AI cloud market beating rivals and investing billio

Cambodia Defends China’s Belt and Road as Economic Lifeline
Cambodia praises China’s Belt and Road projects, calling them vital for growth rejecting claims of d

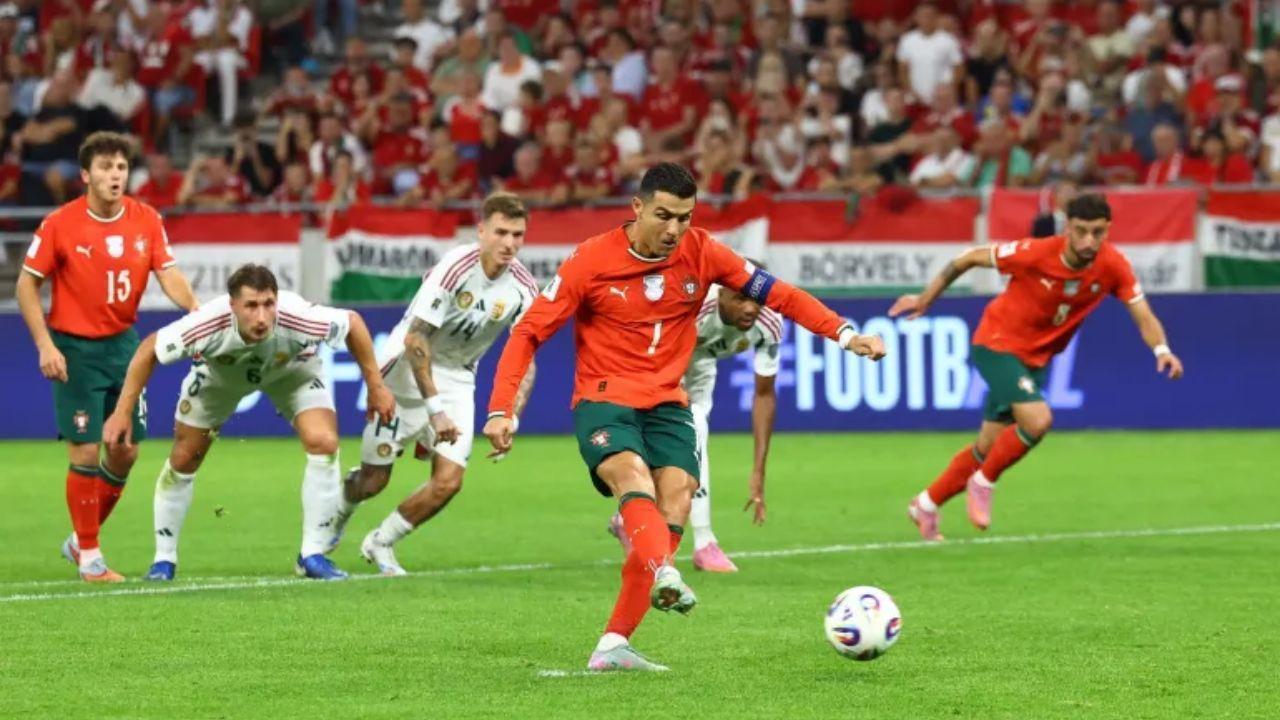
Portugal Norway England shine in UEFA World Cup qualifiers
Portugal beats Hungary 3-2 Ronaldo scores Haaland shines for Norway, Kane leads England in dominant
PV Sindhu exits Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy Lakshya Sen win
PV Sindhu loses early at Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy and Lakshya Sen advance in tough battles India's
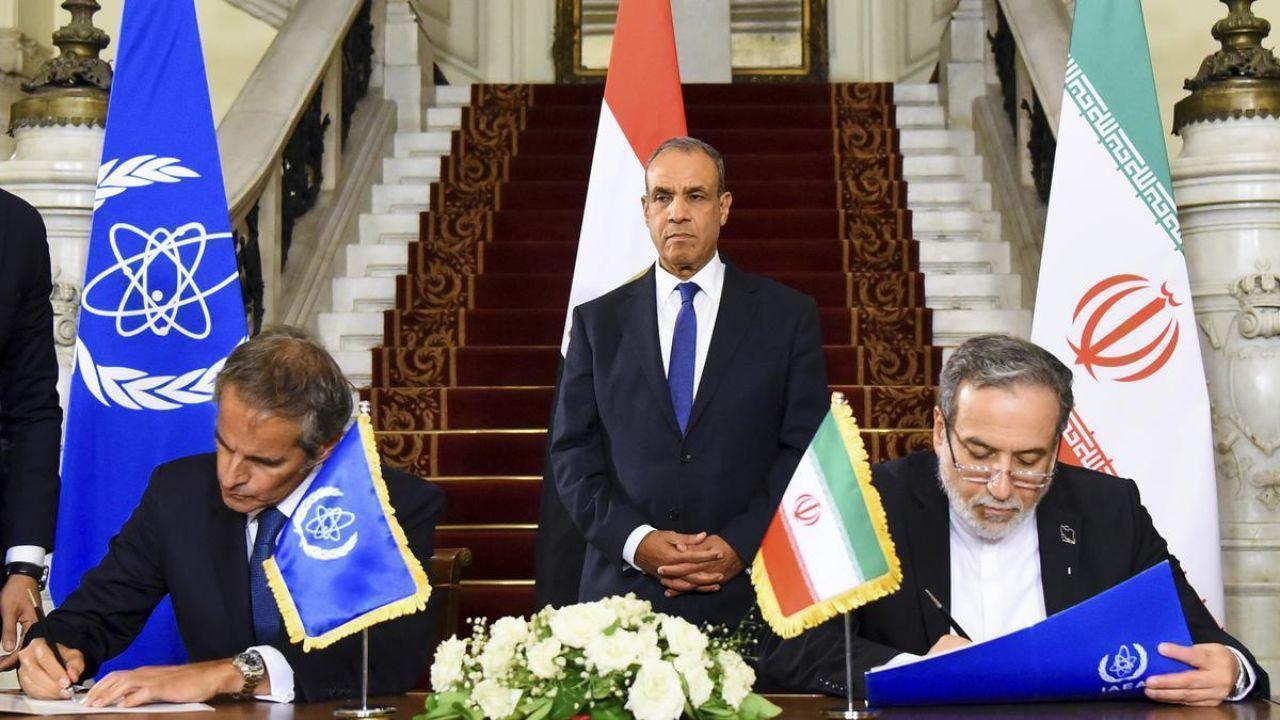

Iran Signs New Cooperation Deal with UN Nuclear Watchdog in Cairo
Iran agrees to a new framework with UN nuclear agency resuming controlled inspections after June’s c
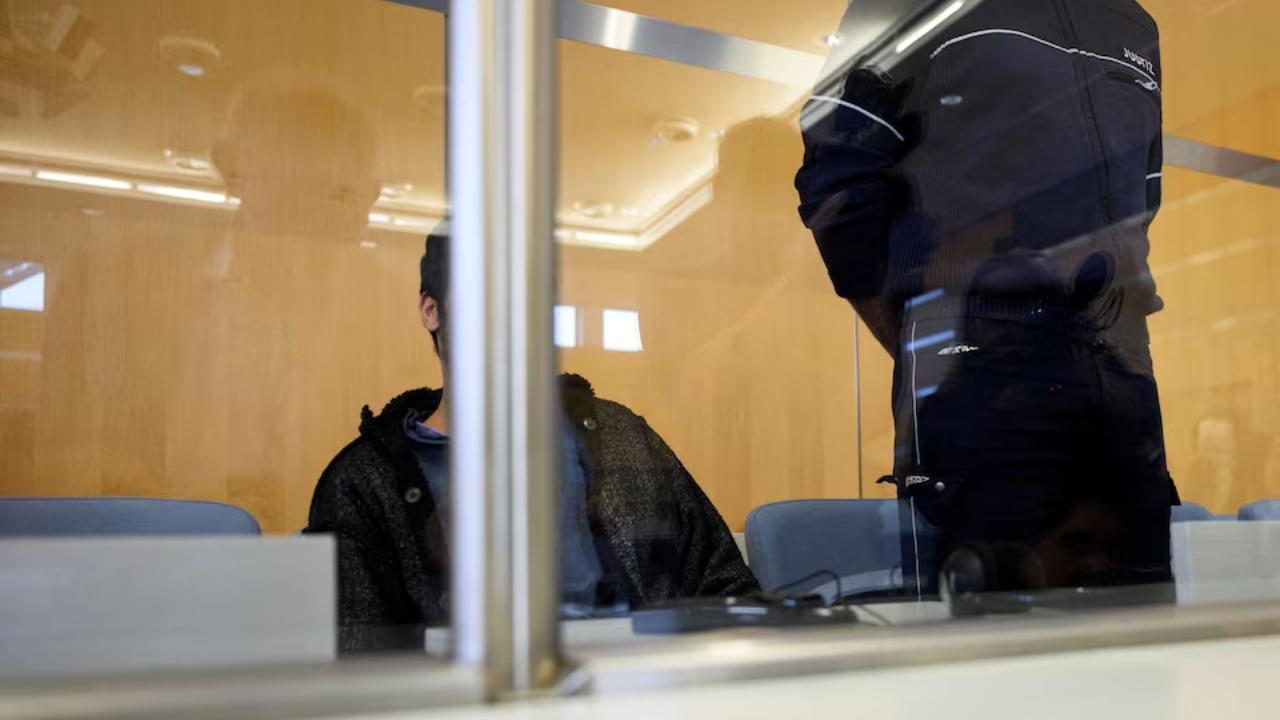

Syrian man found guilty for deadly festival stabbing in Germany
A Syrian man inspired by IS was convicted for stabbing people at a German festival, killing three an