
Post by : Monika
Photo: Reuters
On September 1, 2025, the U.S. dollar weakened and reached its lowest point since July 28. This decline came at a time when investors and traders around the world were closely watching the U.S. economy, particularly upcoming labor market data.
Among the most important reports was the August nonfarm payrolls report, which provides information about the number of jobs added or lost in the United States during the month.
The U.S. dollar’s performance is closely tied to economic data, as it influences expectations for the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. If employment numbers are weaker than expected, it could encourage the Fed to reduce interest rates to stimulate the economy. Conversely, strong employment data might give the Fed more confidence to maintain or increase interest rates.
The recent decline in the dollar shows how sensitive the currency market is to economic and political developments. Investors’ decisions are influenced not only by raw data but also by how they expect the Federal Reserve and other policymakers to react.
Factors Driving the Dollar’s Decline
Several factors contributed to the recent weakening of the U.S. dollar:
1. Anticipation of U.S. Jobs Data
The most significant factor was the anticipation of labor market reports, especially the nonfarm payrolls data. This report is a key indicator of economic health, showing how many new jobs were created or lost in the United States, excluding farm workers and some government employees.
Investors and traders pay close attention to these numbers because they provide clues about the economy’s overall strength. If the report shows fewer jobs added than expected, it can indicate slower economic growth. In such a scenario, the Federal Reserve might lower interest rates to encourage spending and investment, which would reduce the attractiveness of the dollar compared to other currencies.
2. Market Expectations of Rate Cuts
Financial markets were already expecting a high chance of a 25 basis-point rate cut by the Federal Reserve at its September meeting. This expectation was driven by recent economic data suggesting a slowdown in the labor market and concerns about consumer spending.
When markets anticipate a rate cut, the value of the dollar often falls. Lower interest rates make U.S. assets slightly less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a decrease in demand for the dollar. As a result, the currency weakens against other major currencies like the euro and British pound.
3. Political and Legal Uncertainties
Political and legal issues also played a role in weakening the dollar. A recent court ruling declared most of former President Trump’s tariffs illegal, creating uncertainty about trade policies. In addition, President Trump’s attempts to remove Federal Reserve Governor Lisa Cook caused concerns about the independence of the central bank.
The Federal Reserve’s independence is critical for maintaining investor confidence. If investors believe political interference could influence monetary policy, they may become more cautious about holding U.S. dollars or U.S.-denominated assets, contributing to a decline in the currency’s value.
4. Global Market Sentiment
Global market sentiment also affected the dollar. Investors are constantly comparing the U.S. economy with other major economies. As the dollar weakened, other currencies such as the euro and the British pound gained slightly.
This shows that investors were moving funds to currencies they perceived as more stable or less influenced by U.S. economic uncertainty.
Global events, including trade tensions, geopolitical conflicts, and changes in other countries’ interest rates, all interact with domestic U.S. factors to influence the dollar. Even small changes in investor sentiment can create significant movements in the foreign exchange market.
Market Reactions
The immediate reaction to these factors was a noticeable drop in the dollar index. The dollar index measures the currency against a basket of major international currencies, and it fell by 0.22% to 97.64. This decline highlights how even small pieces of economic or political news can influence global financial markets.
The euro and British pound strengthened slightly against the dollar. Investors favored these currencies as a hedge against uncertainties surrounding U.S. economic data and Federal Reserve decisions. In financial markets, when one major currency falls, others often gain as capital flows shift toward perceived safer or more profitable investments.
Equity markets, bond markets, and commodities like gold also react to dollar fluctuations. For example, a weaker dollar can make U.S. exports cheaper for other countries, potentially boosting American companies that sell abroad. Conversely, imports become more expensive, which can raise costs for consumers and businesses in the United States.
Potential Impact on the Economy
The weakening of the U.S. dollar has several broader implications for the economy:
1. Trade and Exports
A weaker dollar can make U.S. goods and services more competitive internationally. Exports may increase as foreign buyers find American products cheaper in their local currencies. This could help boost manufacturing, agriculture, and other export-driven industries.
However, imports become more expensive, which could increase costs for businesses that rely on foreign materials or components. Higher import costs may eventually be passed on to consumers, potentially increasing inflation.
2. Consumer Spending
Fluctuations in the dollar can indirectly affect consumer spending. A weaker currency can lead to higher prices for imported goods, which might reduce household purchasing power. On the other hand, stronger export demand could lead to higher profits for companies, which could result in increased hiring or wage growth over time.
3. Investment and Interest Rates
The dollar’s value also influences international investment flows. If investors expect interest rates to fall, they may shift their money to assets in other currencies with higher returns. This can affect stock and bond prices, creating volatility in financial markets.
The Federal Reserve must balance these effects when deciding on interest rates. While a weaker dollar may support exports, it could also contribute to inflation if import costs rise too quickly.
Traders and investors will closely watch the upcoming U.S. labor market reports for guidance on the economy’s strength. A stronger-than-expected jobs report could support the dollar by showing that the economy is growing and that interest rates may remain stable.
Conversely, weaker employment figures could increase expectations for rate cuts, putting further downward pressure on the dollar. Central bank decisions, political developments, and global economic conditions will continue to interact, making the currency market highly sensitive to new information.
Financial experts advise caution, as sudden shifts in sentiment or unexpected data can lead to rapid changes in the dollar’s value. Investors often use hedging strategies to protect against these fluctuations, but market volatility remains a concern.
The U.S. dollar’s decline to its lowest level since late July 2025 highlights the importance of economic data and political stability in shaping currency values. Anticipation of labor market reports, expectations of Federal Reserve rate cuts, political uncertainties, and global market sentiment all played a role in the recent drop.
As investors wait for key employment numbers, the Federal Reserve’s upcoming decisions on interest rates will be closely scrutinized. These decisions will be critical in determining whether the dollar stabilizes, strengthens, or continues to decline in the near term.
Understanding the dollar’s movements is important not only for traders and investors but also for policymakers, businesses, and consumers. The currency affects trade, inflation, investment, and overall economic stability. Monitoring these trends provides insight into the health of the U.S. economy and the broader global financial system.
the U.S. dollar’s recent decline serves as a reminder of how interconnected economic data, political events, and investor sentiment are. While short-term fluctuations may cause concern, long-term trends will depend on the balance between growth, employment, inflation, and monetary policy decisions.
U.S. dollar decline










Alibaba Cloud Leads China’s AI Market with 36% Share
Alibaba Cloud captured over one-third of China’s AI cloud market beating rivals and investing billio

Cambodia Defends China’s Belt and Road as Economic Lifeline
Cambodia praises China’s Belt and Road projects, calling them vital for growth rejecting claims of d

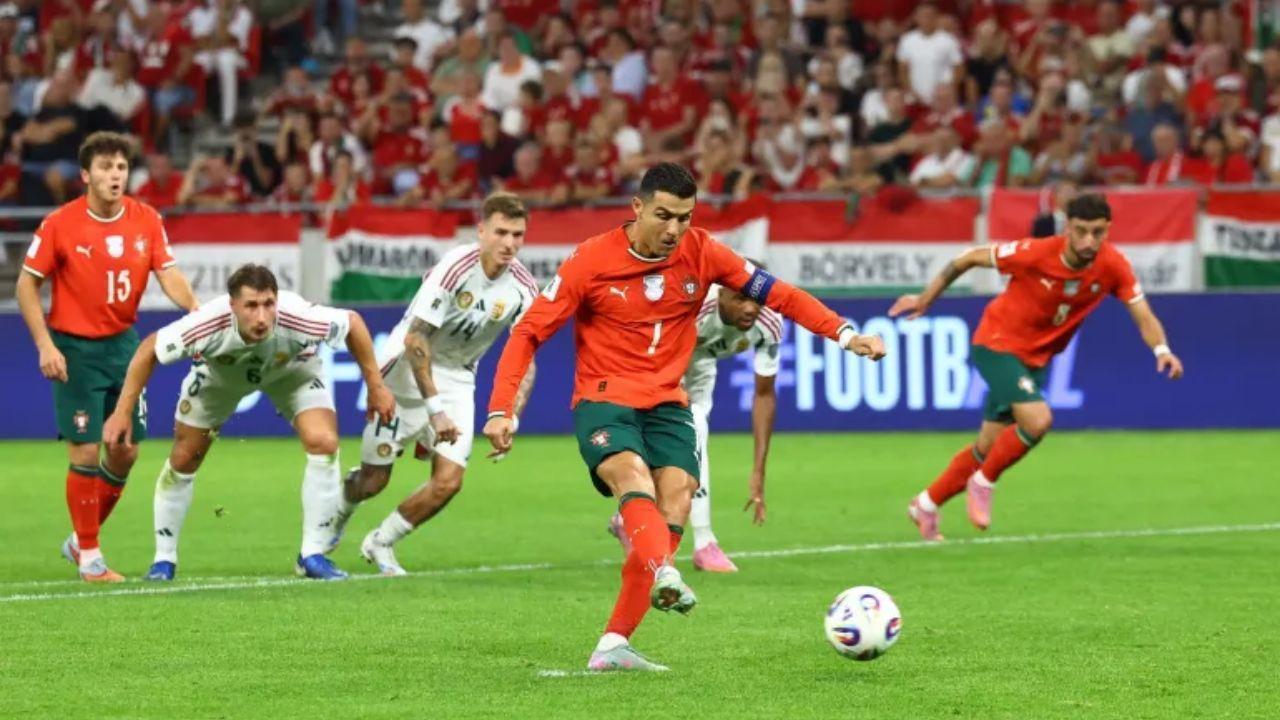
Portugal Norway England shine in UEFA World Cup qualifiers
Portugal beats Hungary 3-2 Ronaldo scores Haaland shines for Norway, Kane leads England in dominant
PV Sindhu exits Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy Lakshya Sen win
PV Sindhu loses early at Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy and Lakshya Sen advance in tough battles India's

Iran Signs New Cooperation Deal with UN Nuclear Watchdog in Cairo
Iran agrees to a new framework with UN nuclear agency resuming controlled inspections after June’s c

Syrian man found guilty for deadly festival stabbing in Germany
A Syrian man inspired by IS was convicted for stabbing people at a German festival, killing three an