
Post by : Anish
Higher education has always been the stepping stone toward career success, but in the past decade, the landscape has shifted dramatically. The rapid pace of technological advancement, global economic changes, and evolving workforce requirements have forced colleges and universities to rethink their approach. Today’s job market demands graduates who are not only academically qualified but also industry-ready from day one. This change has sparked a major transformation in higher education: career-aligned programs. These programs are designed with a singular focus—bridging the gap between theoretical learning and real-world application.
Unlike traditional curricula that emphasize broad-based education, career-aligned degrees integrate job-specific skills, certifications, and experiential learning opportunities into their core. They prepare students for the demands of the workplace while still providing a solid academic foundation. For students and professionals navigating this competitive job market, understanding these programs can be a game-changer.
For decades, the academic model prioritized theoretical knowledge over practical experience. While this produced well-rounded graduates, it often left them underprepared for the fast-paced corporate world. Employers frequently cited a “skills gap,” noting that new hires lacked hands-on abilities needed to perform job roles effectively.
This disconnect triggered widespread criticism of higher education institutions and sparked reforms. Today, the focus has shifted toward developing market-oriented curricula. Institutions now collaborate with businesses, technology providers, and industry leaders to design programs that address current and future job market needs.
In this new model, students are not just learning theories—they are completing internships, engaging in simulations, and earning certifications in tools and technologies that employers value. This blend of education and experience ensures graduates are job-ready upon completing their degrees.
Career-aligned programs are not simply traditional degrees with added internships—they are holistic systems designed to integrate academic learning with career development. Here are some defining characteristics:
Programs are crafted in consultation with companies, ensuring that the syllabus reflects the latest industry standards. For example, computer science students learn not just programming languages but also cloud computing, cybersecurity, and AI tools widely used in businesses today.
Hands-on experience is at the heart of these programs. Students participate in internships or cooperative education placements, giving them exposure to real workplace environments and challenges.
Employers increasingly demand certifications in specialized software or methodologies. Modern programs integrate these certifications into the coursework, enabling students to graduate with both a degree and recognized credentials like AWS Cloud Practitioner, Google Analytics, or Six Sigma.
Technical proficiency is essential, but so is communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Many career-aligned programs now include modules for leadership, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence to ensure graduates thrive in collaborative settings.
Unlike static traditional programs, career-aligned curricula are dynamic. Academic institutions regularly update courses to reflect emerging technologies and trends, ensuring graduates remain competitive in an evolving job market.
Students today are practical and outcome-oriented. They recognize that a degree alone no longer guarantees employment—what matters is employability. Career-aligned programs offer distinct advantages:
Higher Employability: Graduates often secure jobs faster and command better salaries.
Skill Confidence: Students leave college knowing they can handle real-world projects.
Reduced Training Time: Employers appreciate candidates who need minimal on-the-job training.
Global Opportunities: Certifications and industry-standard training make graduates competitive internationally.
According to recent surveys, students enrolled in career-focused programs report higher satisfaction rates compared to those in traditional programs, largely because they feel better prepared for professional life.
The demand for career-oriented education is strongest in sectors undergoing rapid technological transformation. Here are a few industries where specialized programs are booming:
Careers in AI, cybersecurity, cloud computing, and data science dominate the modern job market. Universities now offer degrees that combine core computer science with training in cutting-edge technologies, often in partnership with tech giants like Microsoft or IBM.
From nursing programs emphasizing telemedicine to healthcare management degrees focused on digital health records, the medical sector requires graduates with both technical and patient-care expertise.
The rise of fintech and blockchain has revolutionized finance. Students pursue programs that blend accounting fundamentals with digital payment systems, data analytics, and cryptocurrency management.
With global emphasis on sustainability, energy companies seek professionals skilled in green technologies. Universities now offer programs in renewable energy engineering and environmental management, preparing students for the future energy economy.
While the shift toward career alignment is largely positive, it’s not without challenges. Critics argue that an excessive focus on job-specific skills may undermine the broader goals of education, such as fostering critical thinking and cultural understanding. Additionally, updating curricula frequently is resource-intensive for institutions. Smaller colleges may struggle to keep pace with these changes.
Moreover, industries themselves are evolving rapidly, raising the question: Can universities truly keep up with the speed of innovation? Addressing this requires a continuous dialogue between academia and employers, backed by substantial investment in faculty development and infrastructure.
Employers have long complained about the “skills gap,” where graduates lack practical experience. Career-aligned programs are narrowing this gap significantly. By recruiting graduates who already have certifications, internships, and real-world experience, companies save on training costs and accelerate onboarding. This results in higher productivity and lower attrition rates.
Some organizations have gone a step further, sponsoring university programs or creating dedicated talent pipelines. For instance, large tech companies partner with universities to ensure students graduate ready for roles in software development, data analytics, or cybersecurity.
Looking ahead, higher education is expected to become even more integrated with the professional world. Hybrid programs, lifelong learning pathways, and micro-credentials will dominate the landscape. Students may start their careers while still completing degrees, and employers might become active stakeholders in shaping academic curricula.
The trend toward career alignment is not a passing phase—it is a systemic shift in how education and employment intersect. For students willing to embrace this change, the rewards are substantial: stronger career prospects, financial security, and adaptability in a rapidly changing world.
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure accuracy, readers should verify details with official educational institutions and industry sources before making any academic or career decisions.
#CareerReadyDegrees #JobMarketSkills #HigherEducationTrends #FutureProofCareers #SkillBasedLearning #IndustryDrivenEducation #EducationForEmployment #WorkforceDevelopment #CareerFocusedPrograms #PracticalLearning #EmployabilitySkills #MarketRelevantDegrees #CareerPathwayEducation #HigherEdInnovation #SkillsForSuccessest










Alibaba Cloud Leads China’s AI Market with 36% Share
Alibaba Cloud captured over one-third of China’s AI cloud market beating rivals and investing billio

Cambodia Defends China’s Belt and Road as Economic Lifeline
Cambodia praises China’s Belt and Road projects, calling them vital for growth rejecting claims of d

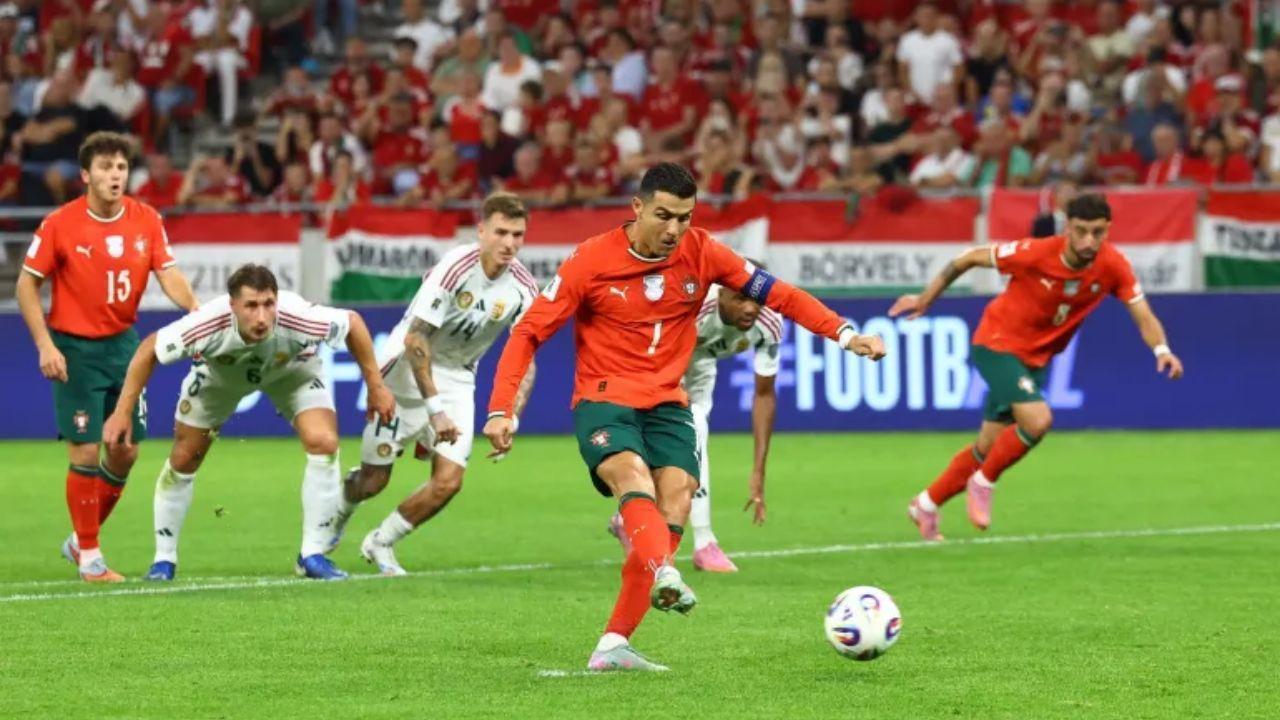
Portugal Norway England shine in UEFA World Cup qualifiers
Portugal beats Hungary 3-2 Ronaldo scores Haaland shines for Norway, Kane leads England in dominant
PV Sindhu exits Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy Lakshya Sen win
PV Sindhu loses early at Hong Kong Open HS Prannoy and Lakshya Sen advance in tough battles India's
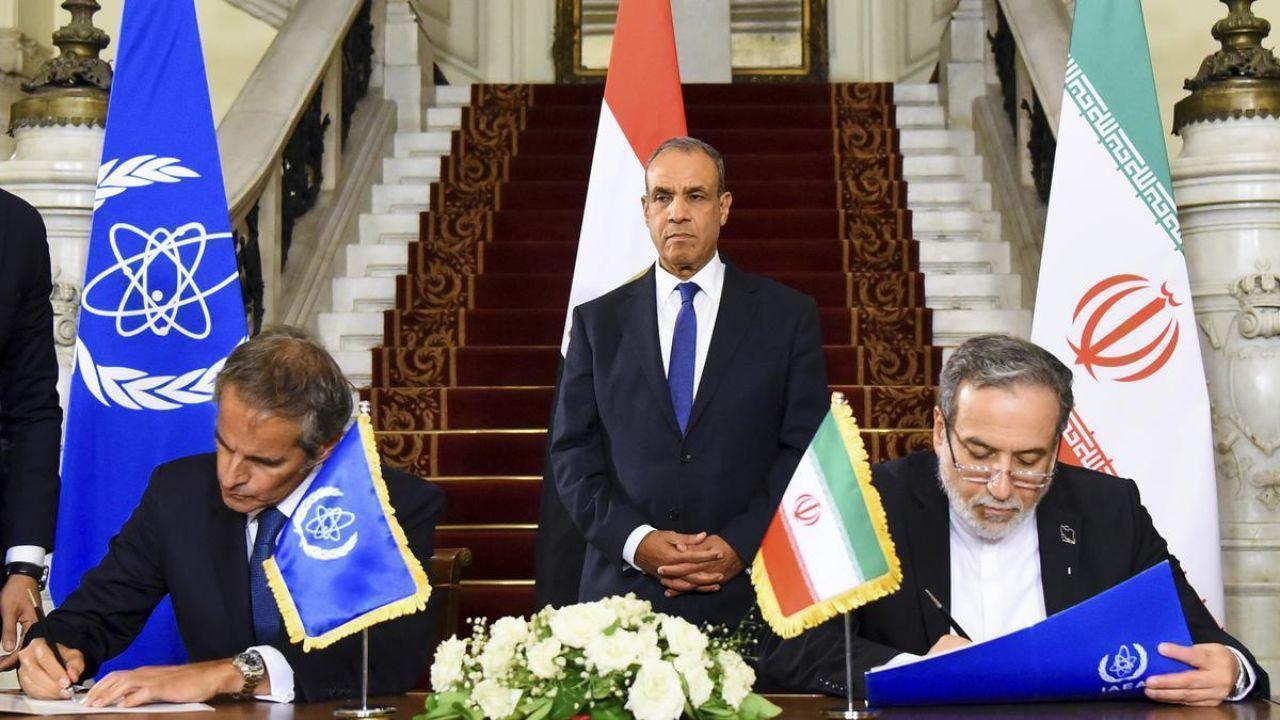

Iran Signs New Cooperation Deal with UN Nuclear Watchdog in Cairo
Iran agrees to a new framework with UN nuclear agency resuming controlled inspections after June’s c
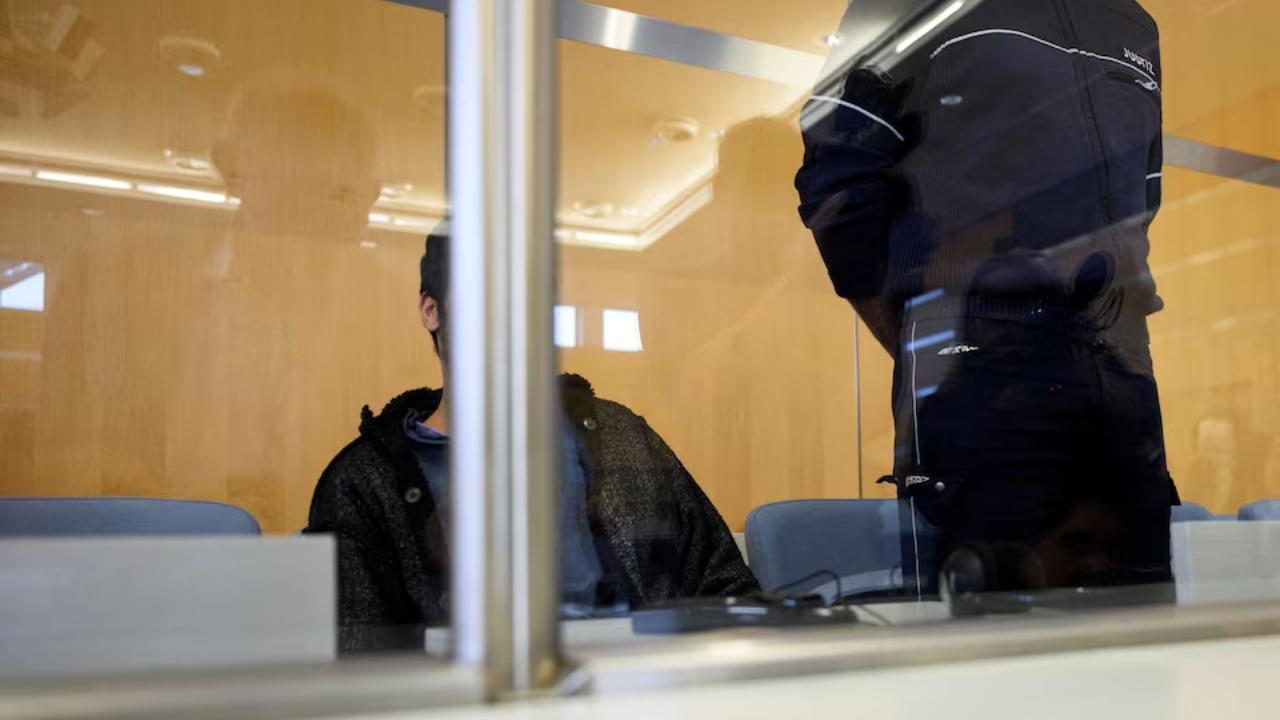

Syrian man found guilty for deadly festival stabbing in Germany
A Syrian man inspired by IS was convicted for stabbing people at a German festival, killing three an