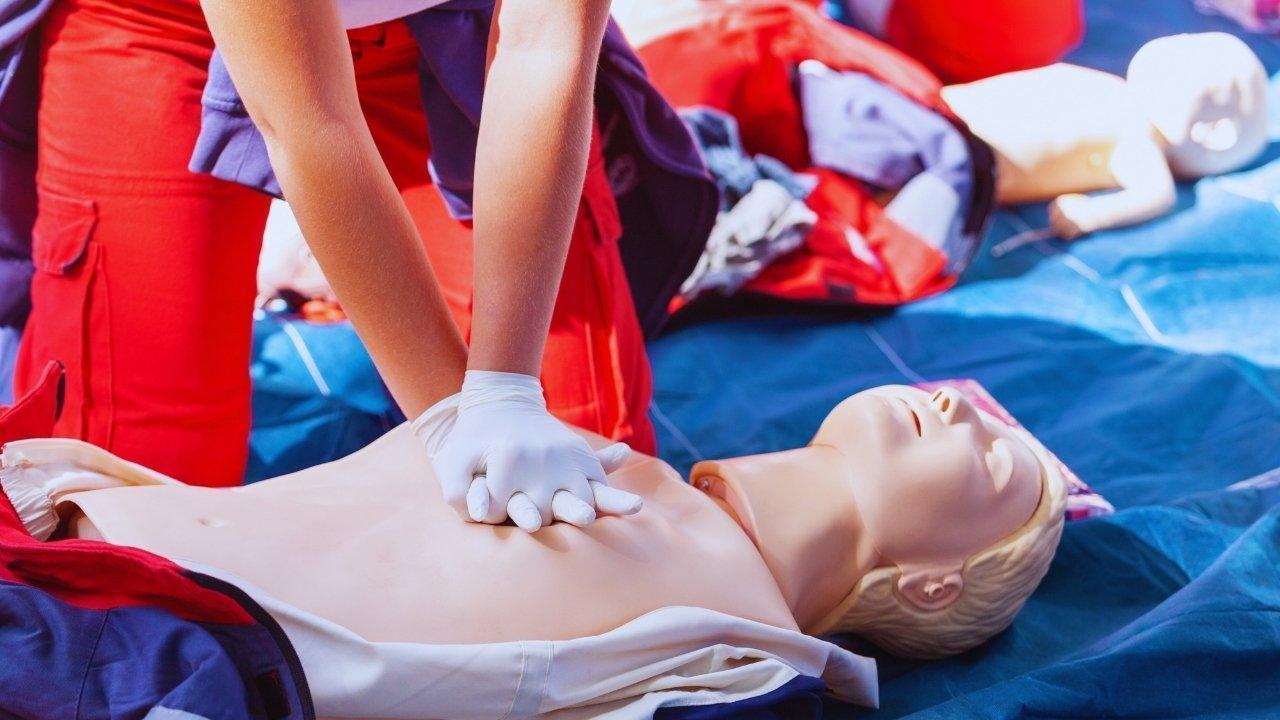
Post by : Anees Nasser
Emergencies rarely announce themselves. They often arrive suddenly, leaving little time to think. In these critical moments, knowing how to respond—even at a basic level—can make a profound difference. CPR, or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, is one of the most essential life-saving skills that ordinary people can learn. When a person’s heart stops beating or their breathing suddenly stops, CPR helps maintain circulation until professional help arrives.
Over the years, medical professionals and global health organisations have emphasised that bystanders—regular people nearby—are often the first and most important link in saving a life. The ability to recognise an emergency, stay calm, call for help, and provide basic assistance can dramatically improve survival chances.
This article offers a comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide to the basics of CPR and emergency response that anyone, regardless of background, can learn. It focuses on high-level awareness and safe practices suitable for general readers. It does not replace professional training but serves as a strong foundation for understanding what to do during critical situations.
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is a combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths (if trained) that help keep blood flowing to the brain and vital organs when a person’s heart or breathing stops.
When a cardiac arrest happens:
The heart suddenly stops beating.
Blood flow to the brain stops almost instantly.
Brain cells begin to die within minutes.
Immediate CPR provides essential oxygen and circulation until emergency medical services arrive. Delaying even a minute reduces survival chances.
Anyone can attempt CPR. You do not need to be a medical professional. Basic hands-only CPR is simple enough that even teenagers can learn it. The goal is not perfection—it is immediate action.
Tap the person gently and speak loudly:
“Are you okay?”
“Can you hear me?”
If they do not respond, treat it as an emergency.
Gasping, irregular breaths, or no breathing at all are signs of distress. Do not waste time checking for a pulse as it can be difficult for non-professionals.
The person is unresponsive.
The person is not breathing normally.
The person has collapsed suddenly.
These are strong indications to begin CPR immediately while someone else calls for medical help.
(This is an awareness guide, not a substitute for certified training.)
Before approaching, quickly ensure:
No live wires
No speeding vehicles
No fire or toxic fumes
Your safety comes first.
If others are present:
Point to someone directly and say:
“You, call emergency services and bring an AED if available.”
When instructions are directed clearly, people respond faster.
If alone and you have a phone:
Call emergency services immediately using speaker mode.
Lay them flat on their back.
Place them on a firm surface.
Hands-only CPR is recommended for most people.
Place the heel of one hand in the centre of the chest.
Place your other hand on top.
Keep your arms straight and your shoulders directly above your hands.
Push hard and fast.
Depth: about two inches for adults.
Pace: around 100–120 compressions per minute (roughly the rhythm of a steady beat).
Let the chest rise fully between compressions.
Do not pause unless:
The person starts breathing
A trained professional takes over
An AED is ready to use
You are too exhausted to continue
Continuous compressions increase survival chances significantly.
An Automated External Defibrillator is a portable device that analyses heart rhythm and, if needed, delivers an electric shock to help restart the heart.
Airports
Malls
Gyms
Corporate offices
Public institutions
AEDs are designed with:
Simple voice instructions
Clear illustrations
Automatic analysis functions
They guide you step by step.
A fainting person:
Breathing resumes
Responds with light stimuli
Usually recovers within seconds
A person in cardiac arrest:
Does not respond
Does not breathe normally
Does not regain consciousness
In doubt? Prioritize safety and call for help.
Brain damage begins within 4–6 minutes without oxygen.
CPR buys time by maintaining circulation.
Your action bridges the gap between collapse and professional care.
Often caused by sudden cardiac arrest.
High-voltage incidents may stop breathing or heartbeat.
Victims may be unconscious and need immediate resuscitation.
If the person becomes unresponsive during a choking episode, CPR may be needed.
Anaphylaxis can sometimes lead to collapse.
Understanding the context helps you act faster.
CPR is crucial, but knowing broader emergency responses strengthens your ability to help.
Encourage coughing if they can still breathe.
If coughing fails, a trained person may perform abdominal thrusts.
If the person becomes unconscious, CPR becomes necessary.
Always seek professional training; baby techniques differ significantly.
Remember the FAST method:
Face drooping
Arm weakness
Speech difficulty
Time to call emergency services
Immediate medical assistance is essential.
Apply firm pressure with clean cloth.
Elevate limb if possible.
Avoid tourniquets unless trained.
Stopping blood loss buys critical time.
Cool burn with running water.
Cover with clean cloth.
Applying ice directly
Using toothpaste, oils or home remedies
Severe burns require immediate professional care.
If a person is breathing but unresponsive:
Turn them gently onto their side.
Tilt head slightly to open airway.
Ensure they stay stable.
This prevents choking on saliva or vomit.
This can worsen injuries.
If the person is unconscious, this increases choking risk.
Immediate communication saves lives.
Always check responsiveness before starting.
Give the patient space and allow fresh air.
Gloves
Clean cloth
Basic bandages
Small flashlight
Emergency contact list
Pain-relief tablets (general)
Sanitiser
Keep walkways clutter-free
Avoid loose wires
Have accessible first-aid supplies
Know where your building’s emergency exits are
How to recognise emergencies
Who to call
How to stay calm
Even children benefit from basic awareness.
Panic delays response and confuses others.
Instead of “Someone call help,” say “You, please call emergency services now.”
Emergency response is not about perfection. It’s about steady action.
Emergency situations can last several minutes, and your effort matters throughout.
More trained individuals mean greater chances of survival in public spaces.
Introducing CPR basics in educational institutes empowers students early.
Companies offering training create safer environments for staff.
Knowing CPR as a household unit increases readiness, especially for elders or children.
CPR and basic emergency response skills are among the most valuable life tools any person can learn. While medical professionals deliver advanced care, the moments before they arrive depend entirely on bystanders. Recognising emergencies quickly, calling for help, performing hands-only CPR when needed, and understanding basic first-aid principles can significantly improve outcomes.
These skills don’t require medical backgrounds—only awareness, willingness and the courage to act. Whether in homes, workplaces, public spaces or travel, being prepared transforms ordinary people into first responders during the most critical moments. Investing a little time into learning CPR and emergency preparedness doesn’t just build confidence; it saves lives.
This article provides general information about CPR and emergency response. It is not a substitute for professional medical training or certification. Individuals should enrol in certified courses to learn proper techniques safely and accurately.










Rybakina and Pegula Reach Australian Open Semifinals Following Major Upsets
Rybakina upsets Swiatek; Pegula defeats Anisimova. Both advance to the Australian Open semifinals, a

Trump Appeals for Calm After Federal Shooting Incident in Minnesota
In response to the fatal shooting of two citizens by federal agents, President Trump calls for calm

Malaysian Football Association's Executive Resigns Amid FIFA Sanctions
The Football Association of Malaysia's leadership resigns following FIFA sanctions related to player

Australian Wine Exports See 8% Decline Due to Global Demand Shifts
Australia's wine exports fell 8% to A$2.34 billion in 2025 as global demand wanes and key markets st

US Hikes Tariffs on South Korea Amid Delay in Investment
US imposes higher tariffs on South Korean imports as investment and reforms stall, escalating trade

Strengthening the U.S.-Taiwan Alliance in AI and Tech Security
Taiwan and the U.S. bolster their partnership in AI, tech, and economic security while addressing gl