
Post by : Priya
Photo:Reuters
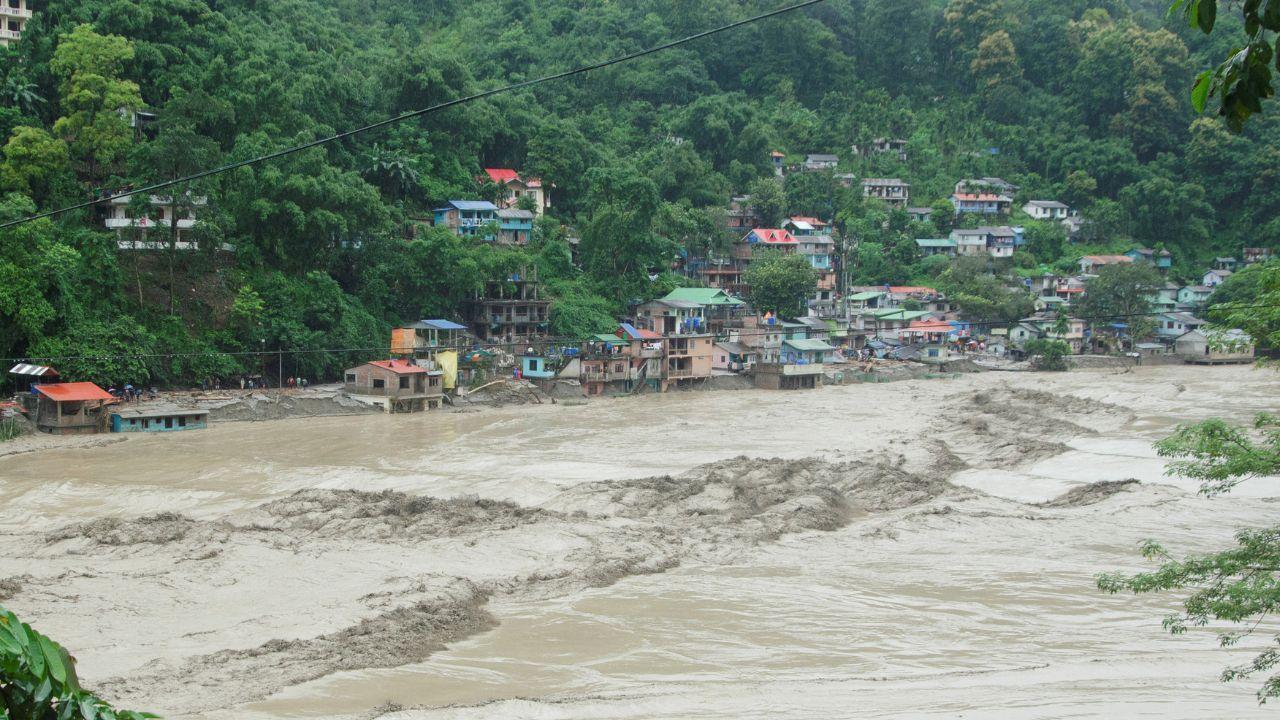
The serene mountainous village of Dharali in Uttarkashi district, Uttarakhand, India, was struck by a catastrophic flash flood and cloudburst event that has left a trail of death, destruction, and despair. The disaster claimed at least 90 lives, with many more missing, and wiped away homes, businesses, and vital infrastructure. Rescue operations continue amid challenging weather and treacherous terrain, underscoring the grave vulnerability of Himalayan settlements to natural calamities intensified by climate change and unplanned development.
The Catastrophe Unfolds
In the early afternoon of August 5, torrential rainwater carrying massive debris surged down the slopes of the Himalayas, converging into the Kheer Ganga river. This deadly mix of water, mud, and rubble violently overflowed and swept through Dharali and nearby villages. Satellite imagery from India’s Cartosat-2S showed an expansive fan of debris stretching nearly 20 hectares and burying large parts of Dharali under mud and rocks, drastically reshaping the landscape of the region.
Initial reports described multiple cloudbursts — localized, intense rainstorms releasing more than 100mm of rainfall per hour in a small area — as the trigger. However, scientific analysis reveals a more complex picture involving not just cloudbursts but possibly a glacial lake outburst flood, landslides, or glacier collapses contributing to this unprecedented flood event. The geological fragility of Himalayan slopes combined with sudden, heavy rain exacerbated the flooding.
Human and Material Losses
The flood razed the Dharali village market area, submerging numerous guesthouses, restaurants, and hotels, placing hundreds of residents and tourists in peril. Over 40 to 50 homes were reported destroyed, while military facilities, including parts of the Harsil Army camp and helipad, suffered significant damages. Tragically, at least eleven soldiers are among the missing. Local authorities believe hundreds could still be trapped under debris.
The region, a gateway for the revered Gangotri pilgrimage, saw the disruption of critical connectivity, isolation of communities, and halted pilgrimage activities. The Indian Army, National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), and State Disaster Response Force (SDRF), supported by drones, search dogs, and heavy machinery, have mounted relentless rescue operations. Despite relentless efforts, persistent rain and rising water levels complicate the search for survivors.
Causes and Warnings from Science
While cloudbursts have historically posed threats to the Himalayas, this event signals an alarming intensification of natural hazards. Experts point to climate change as a critical factor making weather events more extreme and unpredictable. Additionally, unsustainable construction practices along fragile mountain slopes, deforestation, and lack of adequate disaster preparedness have compounded vulnerability.
Meteorological data from the India Meteorological Department showed only moderate rainfall amounts in some areas on the day of the disaster, raising questions about whether a classical cloudburst alone caused such devastation. Researchers are investigating a combination of factors including glacier destabilization and landslides that may have led to a glacial lake outburst flood – a surge caused by sudden glacial meltwater release – as key contributors.
Impact on Lives and Livelihoods
Beyond the tragic loss of human life, the flood has obliterated homes, caused displacement, and destroyed businesses that sustain local communities. The town’s economy, heavily reliant on tourism and pilgrimage, now faces uncertainty and hardship as infrastructure lies in ruins. Many families are left without shelter or access to basic services, highlighting the need for swift and coordinated humanitarian aid.
Government and Community Response
Prompt action by the Indian Army and disaster response teams has been vital in preventing an even higher death toll. Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami and local authorities maintain continuous monitoring of the weather and emergency situation. Evacuations and relief camps are being organized, and efforts to restore connectivity and essential services are underway.
Yet, there is a pressing need for long-term disaster risk management strategies that anticipate such catastrophes. This includes improved weather forecasting, early warning systems, environmentally sensitive urban planning, safer road and infrastructure construction, and community education to build resilience.
The Broader Himalayan Crisis
This disaster mirrors an alarming trend across Uttarakhand and the wider Himalayan region, where flash floods and landslides have emerged as leading causes of loss of life and property in recent years. In the past decade alone, hundreds have died from similar events, raising concerns about the increasing frequency of extreme weather linked to global warming and environmental degradation.
Communities residing in high mountain zones face unique challenges related to steep slopes, fragile geology, and changing climate patterns. The Dharali flood is a stark reminder of the urgent need to safeguard vulnerable populations through science-guided policies and community engagement.
Looking Forward: Preparedness and Sustainability
Addressing the rising threat of Himalayan floods requires a multidimensional approach:
Enhanced Scientific Research: Accurate climate and geological studies to model risks and early indicators.
Sustainable Development: Regulating construction and land use to prevent destabilization of slopes and water channels.
Disaster Preparedness: Strengthening local capacity, warning systems, and rapid response infrastructure.
Climate Action: Global and local efforts to mitigate climate change impacts, including reducing emissions and conserving ecosystems.










Kazakhstan Boosts Oil Supply as US Winter Storm Disrupts Production
Oil prices inch down as Kazakhstan's oilfield ramps up production, countered by severe disruptions f

Return of Officer's Remains in Gaza May Open Rafah Crossing
Israel confirms Ran Gvili's remains identification, paving the way for the Rafah border crossing's p

Border 2 Achieves ₹250 Crore Globally in Just 4 Days: Sunny Deol Shines
Sunny Deol's Border 2 crosses ₹250 crore in 4 days, marking a significant breakthrough in global box
Delay in Jana Nayagan Release as Madras HC Bars Censorship Clearance
The Madras High Court halts the approval of Jana Nayagan's censor certificate, postponing its releas

Tragedy Strikes as MV Trisha Kerstin 3 Accident Leaves 316 Rescued
The MV Trisha Kerstin 3 met an unfortunate fate near Jolo, with 316 passengers rescued. The governme

Aryna Sabalenka Advances to Semi-Finals, Targeting Another Grand Slam Title
Top seed Aryna Sabalenka triumphed over Jovic and now faces Gauff or Svitolina in the semi-finals as